| commit 250b16e1082593636d1487ced191f831b505359e |
| Author: Liang Zhang <terrymanu@163.com> |
| Date: Mon Oct 19 20:52:53 2020 +0800 |
| |
| For checkstyle & fix typo (#1608) |
| |
| * Fix typo |
| |
| * For checkstyle |
| |
| diff --git a/docs/content/features/elastic.en.md b/docs/content/features/elastic.en.md |
| index ef76631fe..ae3ab67ed 100644 |
| --- a/docs/content/features/elastic.en.md |
| +++ b/docs/content/features/elastic.en.md |
| @@ -14,7 +14,7 @@ ElasticJob is aware of the number of servers in an almost-real-time manner, with |
| |
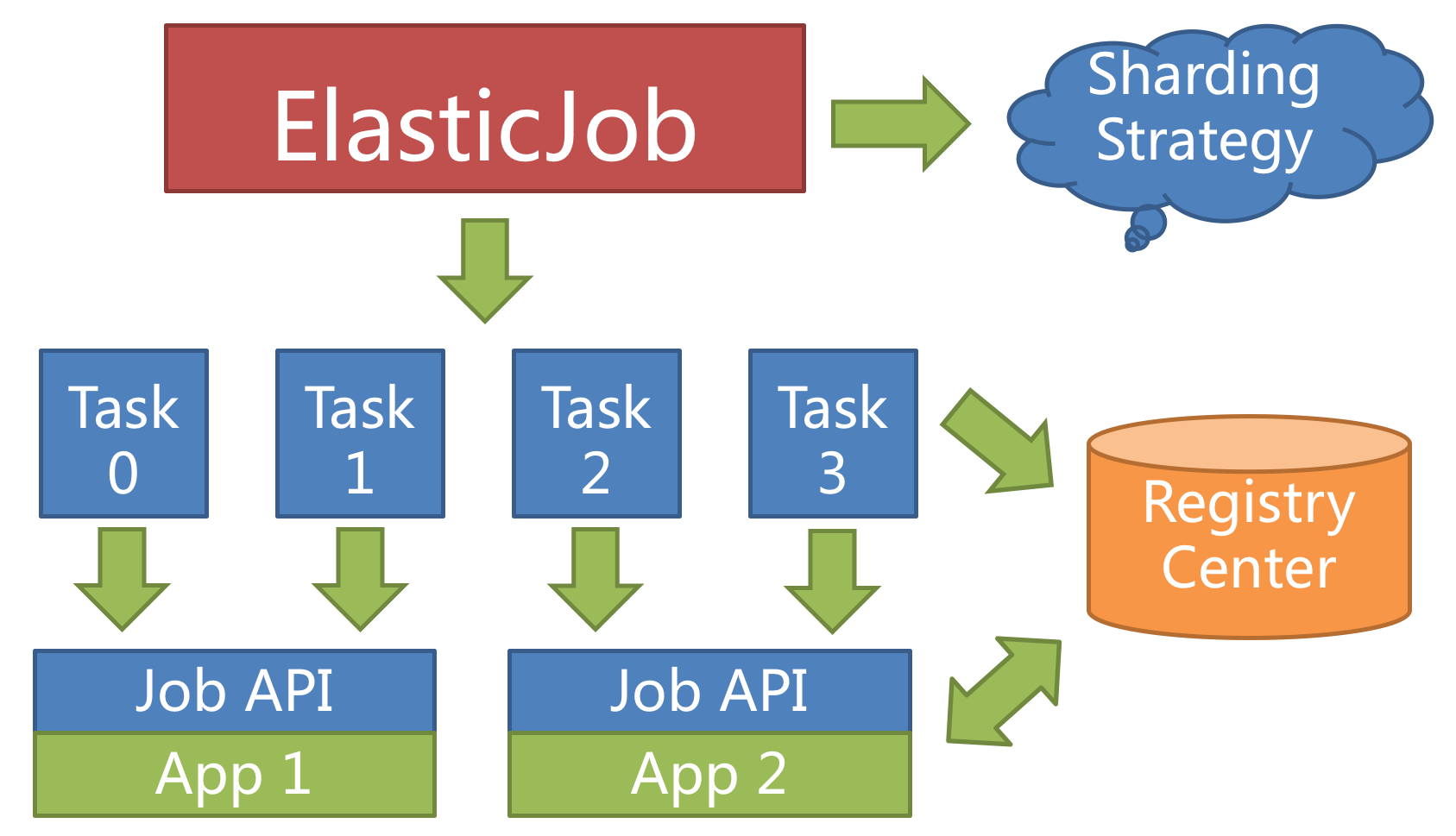
| To execute the job in distributed servers, a job will be divided into multiple individual job items, one or some of which will be executed by the distributed servers. |
| |
| -For example, if a job is divided into 4 slices, and there're two servers to execute the job, then each server is assigned 2 slices, undertaking 50% of the workload, as follows. |
| +For example, if a job is divided into 4 slices, and there are two servers to execute the job, then each server is assigned 2 slices, undertaking 50% of the workload, as follows. |
| |
|  |
| |
| @@ -40,7 +40,7 @@ When new job server joins, ElasticJob will be aware of it from the registry, and |
| |
| Configuring a larger number of sharding items than the number of servers, or better, a multiplier of the number of servers, makes it more reasonably for the job to leverage the resources, and assign the sharding items dynamically. |
| |
| -For example, we have 10 sharding items and there're 3 servers, the number of sharding items are server A = 0,1,2; server B = 3,4,5; server C = 6,7,8,9. |
| +For example, we have 10 sharding items and there are 3 servers, the number of sharding items are server A = 0,1,2; server B = 3,4,5; server C = 6,7,8,9. |
| If the server C is down, then server A = 0,1,2,3,4 and B = 5,6,7,8,9, maximizing the throughput without losing any sharding item. |
| |
| ## High Availability |