Bridge the gap between Graph Databases and Large Language Models
HugeGraph-LLM is a comprehensive toolkit that combines the power of graph databases with large language models. It enables seamless integration between HugeGraph and LLMs for building intelligent applications.
For detailed source code doc, visit our DeepWiki page. (Recommended)
[!IMPORTANT]
- Python: 3.10+ (not tested on 3.12)
- HugeGraph Server: 1.3+ (recommended: 1.5+)
- UV Package Manager: 0.7+
Choose your preferred deployment method:
The fastest way to get started with both HugeGraph Server and RAG Service:
# 1. Set up environment cp docker/env.template docker/.env # Edit docker/.env and set PROJECT_PATH to your actual project path # See "config.md" for all available configuration options # If there is not a configuration file (named .env) under hugegraph-llm, run the following command cd hugegraph-llm && touch .env && cd .. # 2. Deploy services cd docker docker-compose -f docker-compose-network.yml up -d # 3. Verify deployment docker-compose -f docker-compose-network.yml ps # 4. Access services # HugeGraph Server: http://localhost:8080 # RAG Service: http://localhost:8001
For more control over individual components:
hugegraph/rag - Development image with source code accesshugegraph/rag-bin - Production-optimized binary (compiled with Nuitka)# 1. Create network docker network create -d bridge hugegraph-net # 2. Start HugeGraph Server docker run -itd --name=server -p 8080:8080 --network hugegraph-net hugegraph/hugegraph # 3. Start RAG Service docker pull hugegraph/rag:latest docker run -itd --name rag \ -v /path/to/your/hugegraph-llm/.env:/home/work/hugegraph-llm/.env \ -p 8001:8001 --network hugegraph-net hugegraph/rag # 4. Monitor logs docker logs -f rag
For development and customization:
# 1. Start HugeGraph Server docker run -itd --name=server -p 8080:8080 hugegraph/hugegraph # 2. Install UV package manager (if not already installed) curl -LsSf https://astral.sh/uv/install.sh | sh # 3. Clone and setup project git clone https://github.com/apache/incubator-hugegraph-ai.git cd incubator-hugegraph-ai # Configure environment (see config.md for detailed options), .env will auto create if not exists # 4. Install dependencies and activate environment # NOTE: If download is slow, uncomment mirror lines in ../pyproject.toml or use: uv config --global index.url https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple # Or create local uv.toml with mirror settings to avoid git diff (see uv.toml example in root) uv sync --extra llm # Automatically creates .venv and installs dependencies source .venv/bin/activate # Activate once - all commands below assume this environment # 5. Launch RAG demo python -m hugegraph_llm.demo.rag_demo.app # Access at: http://127.0.0.1:8001 # 6. (Optional) Custom host/port python -m hugegraph_llm.demo.rag_demo.app --host 127.0.0.1 --port 18001
[!NOTE] The following commands assume you're in the activated virtual environment from step 4 above
# To use vector database backends (e.g., Milvus, Qdrant), sync the optional dependencies: uv sync --extra vectordb # Download NLTK stopwords for better text processing python ./src/hugegraph_llm/operators/common_op/nltk_helper.py # Update configuration files python -m hugegraph_llm.config.generate --update
[!TIP]
uv syncautomatically creates virtual environment (.venv) and installs all dependencies- Activate once with
source .venv/bin/activate- all subsequent commands assume this environment- Check our Quick Start Guide for detailed usage examples
Use the Gradio interface for visual knowledge graph building:
Input Options:
Schema Configuration:
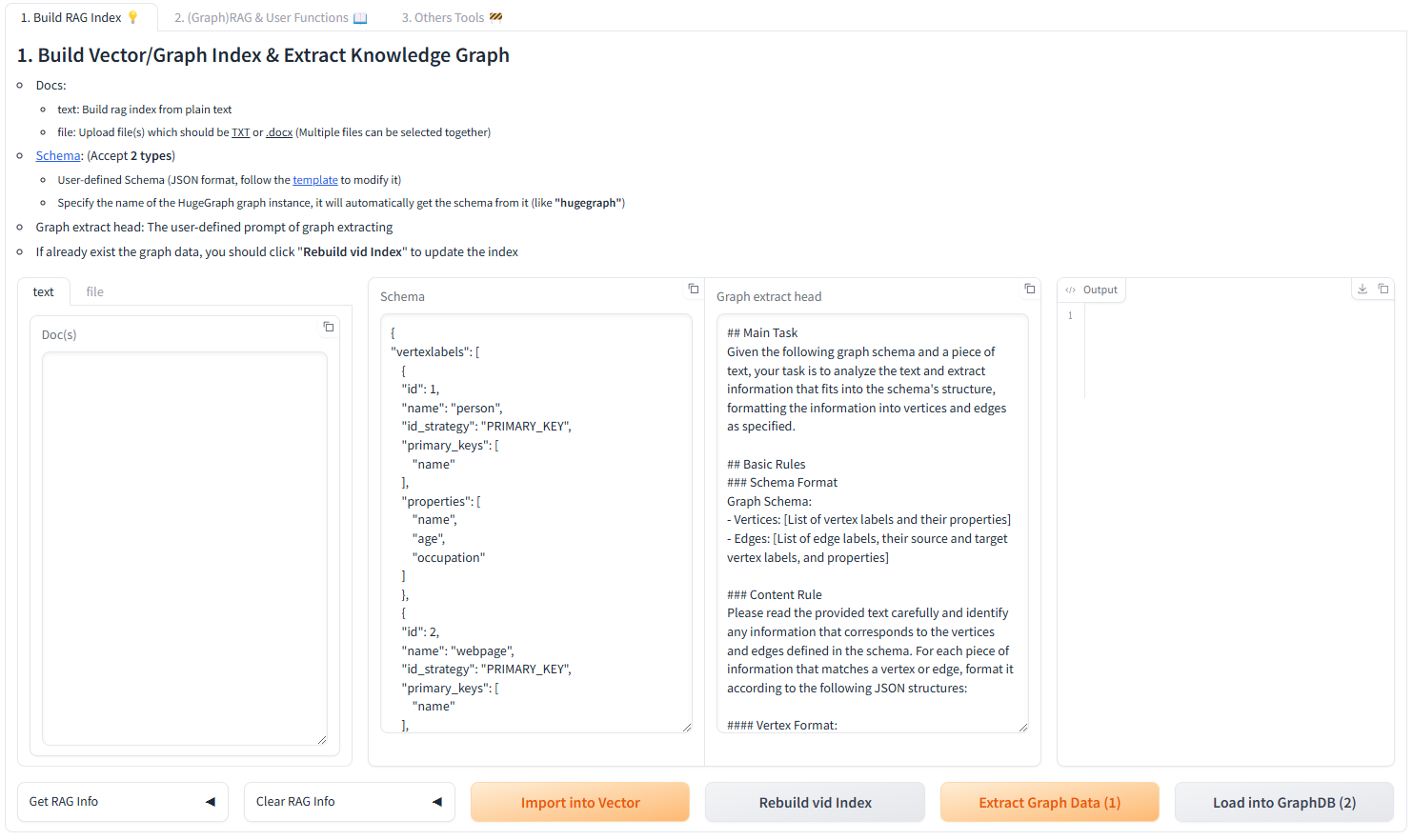
After running the demo, configuration files are automatically generated:
hugegraph-llm/.envhugegraph-llm/src/hugegraph_llm/resources/demo/config_prompt.yamlThe system supports both English and Chinese prompts. To switch languages:
.env file: Change LANGUAGE=en to LANGUAGE=CN (or vice versa)Supported Values:
LANGUAGE=EN - English prompts (default)LANGUAGE=CN - Chinese prompts (中文提示词)[!NOTE] Configuration changes are automatically saved when using the web interface. For manual changes, simply refresh the page to load updates.
LLM Provider Support: This project uses LiteLLM for multi-provider LLM support.
If you previously used high-level classes like RAGPipeline or KgBuilder, the project now exposes stable flows through the Scheduler API. Use SchedulerSingleton.get_instance().schedule_flow(...) to invoke workflows programmatically. Below are concise, working examples that match the new architecture.
from hugegraph_llm.flows.scheduler import SchedulerSingleton scheduler = SchedulerSingleton.get_instance() res = scheduler.schedule_flow( "rag_graph_only", query="Tell me about Al Pacino.", graph_only_answer=True, vector_only_answer=False, raw_answer=False, gremlin_tmpl_num=-1, gremlin_prompt=None, ) print(res.get("graph_only_answer"))
from hugegraph_llm.flows.scheduler import SchedulerSingleton scheduler = SchedulerSingleton.get_instance() res = scheduler.schedule_flow( "rag_vector_only", query="Summarize the career of Ada Lovelace.", vector_only_answer=True, vector_search=True ) print(res.get("vector_only_answer"))
from hugegraph_llm.flows.scheduler import SchedulerSingleton scheduler = SchedulerSingleton.get_instance() response = scheduler.schedule_flow( "text2gremlin", "find people who worked with Alan Turing", 2, # example_num "hugegraph", # schema_input (graph name or schema) None, # gremlin_prompt_input (optional) ["template_gremlin", "raw_gremlin"], ) print(response.get("template_gremlin"))
from hugegraph_llm.flows.scheduler import SchedulerSingleton examples = [{"id": "natural language query", "gremlin": "g.V().hasLabel('person').valueMap()"}] res = SchedulerSingleton.get_instance().schedule_flow("build_examples_index", examples) print(res)
Why the change: the internal execution engine was refactored to a pipeline-based scheduler (GPipeline + GPipelineManager). The scheduler provides a stable entrypoint while keeping flow implementations modular.
If you need help migrating a specific snippet, open a PR or issue and include the old code — we can provide a targeted conversion.
[!IMPORTANT] > For developers contributing to hugegraph-llm with AI coding assistance:
- Start Here: First read
../rules/README.mdfor the complete AI-assisted development workflow- Module Context: Rename
AGENTS.mdin this directory as context for your LLM (e.g.,CLAUDE.md,copilot-instructions.md)- Code Analysis: Follow comprehensive analysis methodology in
../rules/prompts/project-deep.md- Documentation: Maintain structured documentation standards from
../rules/prompts/project-general.md- Quality Standards: Ensure type annotations, proper testing, and consistent patterns
- Business Logic: Focus on graph-LLM integration logic and RAG pipeline optimization
These guidelines ensure consistent code quality and maintainable graph-AI integrations.
License: Apache License 2.0 | Community: Apache HugeGraph