<!---Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership. The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License. --->
Funnel
The Funnel Function
funnel(edges_segmentN, user_specification, node_labels= False)
Creates Funnel Graph from defined edge list and optional user-provided labels edges_segmentN: List of Tuples user_specification: String of Target of interest e.g. #document node_labels: Optional Dictionary of key default values, value replacements Returns a Funnel graph.
Remove the duplicates
edge_list_temp = [] for row in edges_segmentN: if row[0] != row[1]: edge_list_temp.append(row) edge_list = edge_list_temp
Convert from list of 2s to list of 1s
edgelist_list = [] length = len(edge_list) - 1 for i in edge_list: if edge_list.index(i) != length: edgelist_list.append(i[0]) else: edgelist_list.append(i[0]) edgelist_list.append(i[1])
Remove the none values
funnel_targets_temp = [] for item in edgelist_list: if item != None: funnel_targets_temp.append(item) funnel_targets = funnel_targets_temp
Convert that list into a list of 3s
edge_list = [] for i in range(len(funnel_targets)): if i == (len(funnel_targets) - 2): break else: edge_list.append((funnel_targets[i], funnel_targets[i + 1], funnel_targets[i + 2]))
Convert the list of 3s to a counter
edge_list_counter = collections.Counter(edge_list) first_rung = user_specification new_edge_list = [] for i in edge_list: if i[0] == user_specification: new_edge_list.append((i[0], i[1], i[2])) new_edge_list_counter = collections.Counter(new_edge_list) new_edge_list_counter.most_common(1) first_rung = new_edge_list_counter.most_common(1)[0][0][0] second_rung = new_edge_list_counter.most_common(1)[0][0][1] third_rung = new_edge_list_counter.most_common(1)[0][0][2] counter1 = 0 counter2 = 0 counter3 = 0 for i in edge_list: if i[0] == first_rung: counter1 += 1 if i[1] == second_rung: counter2 += 1 if i[2] == third_rung: counter3 += 1
Numbers are how many times each target occured Edges are the targets
numbers = [counter1, counter2, counter3] edges = [first_rung, second_rung, third_rung]
If node labels was given as an argument, replaces the targets with the provided names
if node_labels: new_edges = [] for edge in edges: if edge in node_labels: new_edges.append(node_labels[edge]) else: new_edges.append(edge) edges = new_edges
Plotting labels from the list with the values from the dictionary
data = dict( number=numbers, edge=edges)
Plotting the figure
fig = go.Figure(go.Funnel( y=edges, x=numbers, textposition="inside", textinfo="value+percent initial", opacity=0.65, marker={"color": ["deepskyblue", "lightsalmon", "tan"], "line": {"width": [2]}}, connector={"line": {"color": "lime", "dash": "dot", "width": 5}}) ) fig.show()
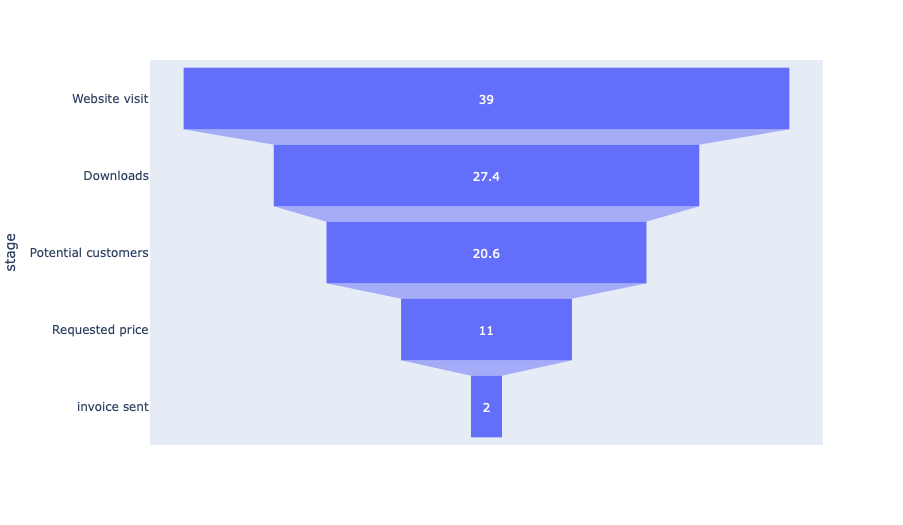
Funnel Example
funnel(edges_segmentN, user_specification, node_labels=False)
The Funnel Function takes the arguments: edges_segmentN: List of Tuples user_specification: A string of target of interest e.g. #document node_labels (Optional): Optional Dictionary of key default values with value replacements And it will return a Funnel graph. Below is an example of a Funnel Diagram:
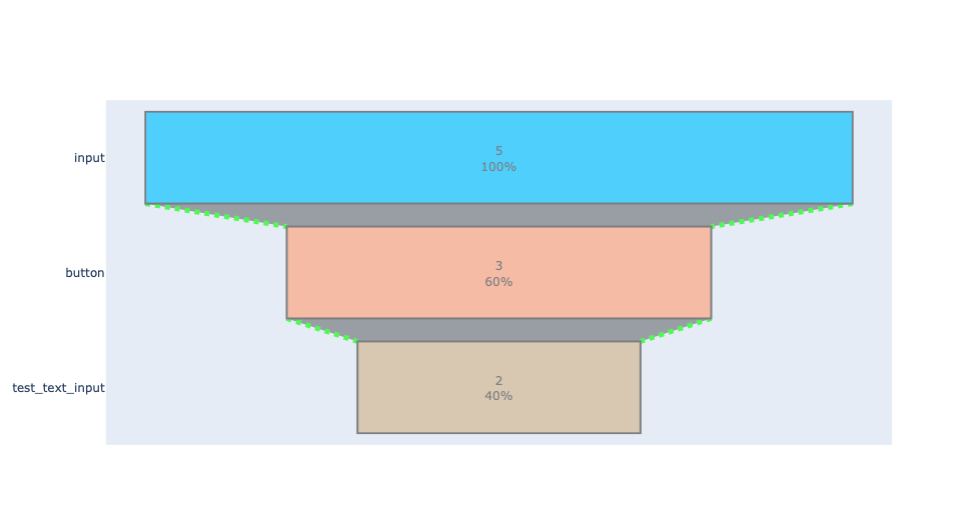
 Additionally, users have the option to pass a dictionary of node labels to replace existing labels.
Additionally, users have the option to pass a dictionary of node labels to replace existing labels.
Below is an example:
Input:
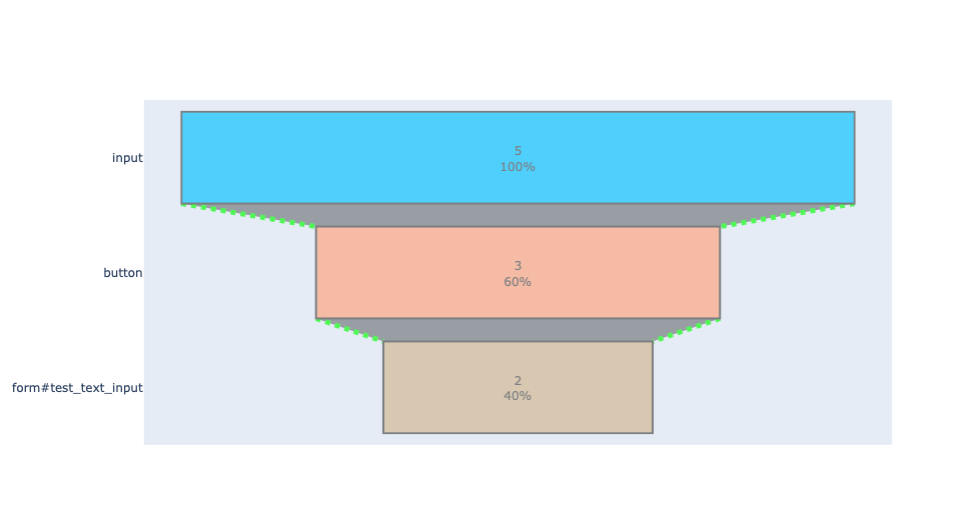
edges = [('#document', 'button#test_button'), ('button#test_button', '#document'), ('#document', 'input'), ('input', 'button'), ('button', 'input'), ('input', 'form#test_text_input'), ('form#test_text_input', 'input'), ('input', 'button'), ('button', 'form#test_text_input'), ('form#test_text_input', '#document'), ('#document', 'form#test_radio_input'), ('form#test_radio_input', 'input'), ('input', 'button#Mock Request Button'), ('button#Mock Request Button', '#document'), ('#document', 'input'), ('input', 'button'), ('button', 'form#test_text_input'), ('form#test_text_input', 'p'), ('p', '#document'), ('#document', 'button#test_button'), ('button#test_button', '#document'), ('#document', 'form#test_radio_input'), ('form#test_radio_input', 'input'), ('input', 'form#test_radio_input'), ('form#test_radio_input', 'input')] userspec = 'input' funnel(edges, userspec)
Now we can add the optional node labels to be replaced. Input:
edges = [('#document', 'button#test_button'), ('button#test_button', '#document'), ('#document', 'input'), ('input', 'button'), ('button', 'input'), ('input', 'form#test_text_input'), ('form#test_text_input', 'input'), ('input', 'button'), ('button', 'form#test_text_input'), ('form#test_text_input', '#document'), ('#document', 'form#test_radio_input'), ('form#test_radio_input', 'input'), ('input', 'button#Mock Request Button'), ('button#Mock Request Button', '#document'), ('#document', 'input'), ('input', 'button'), ('button', 'form#test_text_input'), ('form#test_text_input', 'p'), ('p', '#document'), ('#document', 'button#test_button'), ('button#test_button', '#document'), ('#document', 'form#test_radio_input'), ('form#test_radio_input', 'input'), ('input', 'form#test_radio_input'), ('form#test_radio_input', 'input')] userspec = 'input' labels = {'form#test_text_input':'test_text_input'} funnel(edges, userspec, labels)