title: Deployment modes keywords:
- API gateway
- Apache APISIX
- APISIX deployment modes description: Documentation about the three deployment modes of Apache APISIX.
APISIX has three different deployment modes for different production use cases. The table below summarises the deployment modes:
| Deployment mode | Roles | Description |
|---|---|---|
| traditional | traditional | Data plane and control plane are deployed together. enable_admin attribute should be disabled manually. |
| decoupled | data_plane / control_plane | Data plane and control plane are deployed independently. |
| standalone | data_plane | Only data plane is deployed and the configurations are loaded from a local YAML file. |
Each of these deployment modes are explained in detail below.
Traditional
In the traditional deployment mode, one instance of APISIX will be both the data plane and the control plane.
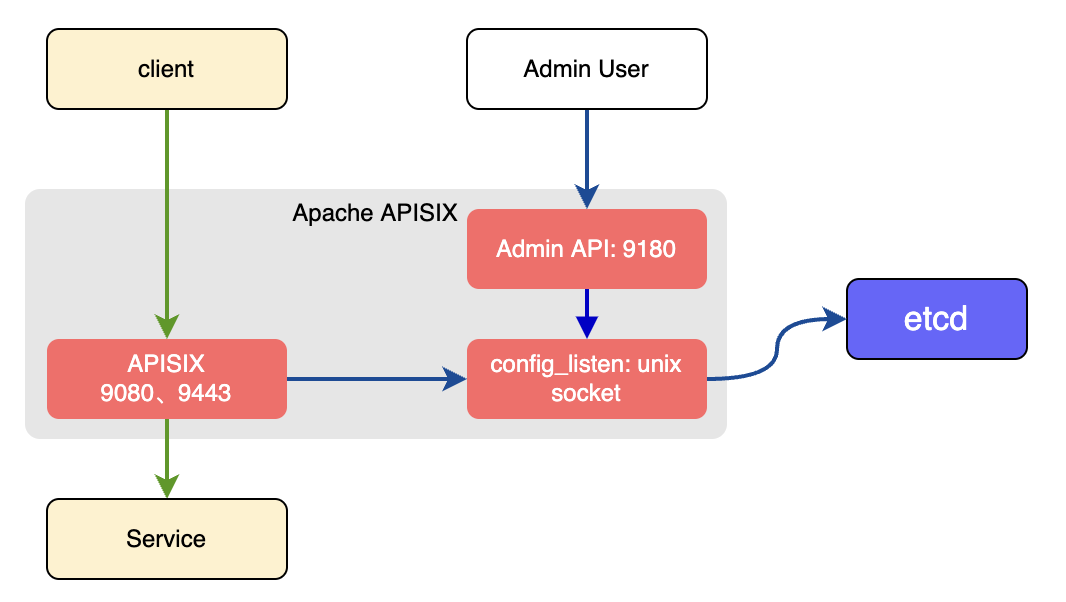
There will be a conf server that listens on the UNIX socket and acts as a proxy between APISIX and etcd. Both the data and the control planes connect to this conf server via HTTP.
An example configuration of the traditional deployment mode is shown below:
apisix: node_listen: - port: 9080 deployment: role: traditional role_traditional: config_provider: etcd admin: admin_listen: port: 9180 etcd: host: - http://${etcd_IP}:${etcd_Port} prefix: /apisix timeout: 30
The instance of APISIX deployed as the traditional role will:
- Listen on port
9080to handle user requests, controlled bynode_listen. - Listen on port
9180to handle Admin API requests, controlled byadmin_listen.
Decoupled
In the decoupled deployment mode the data plane and control plane instances of APISIX are deployed separately. i.e one instance of APISIX is configured to be a data plane and the other to be a control plane.
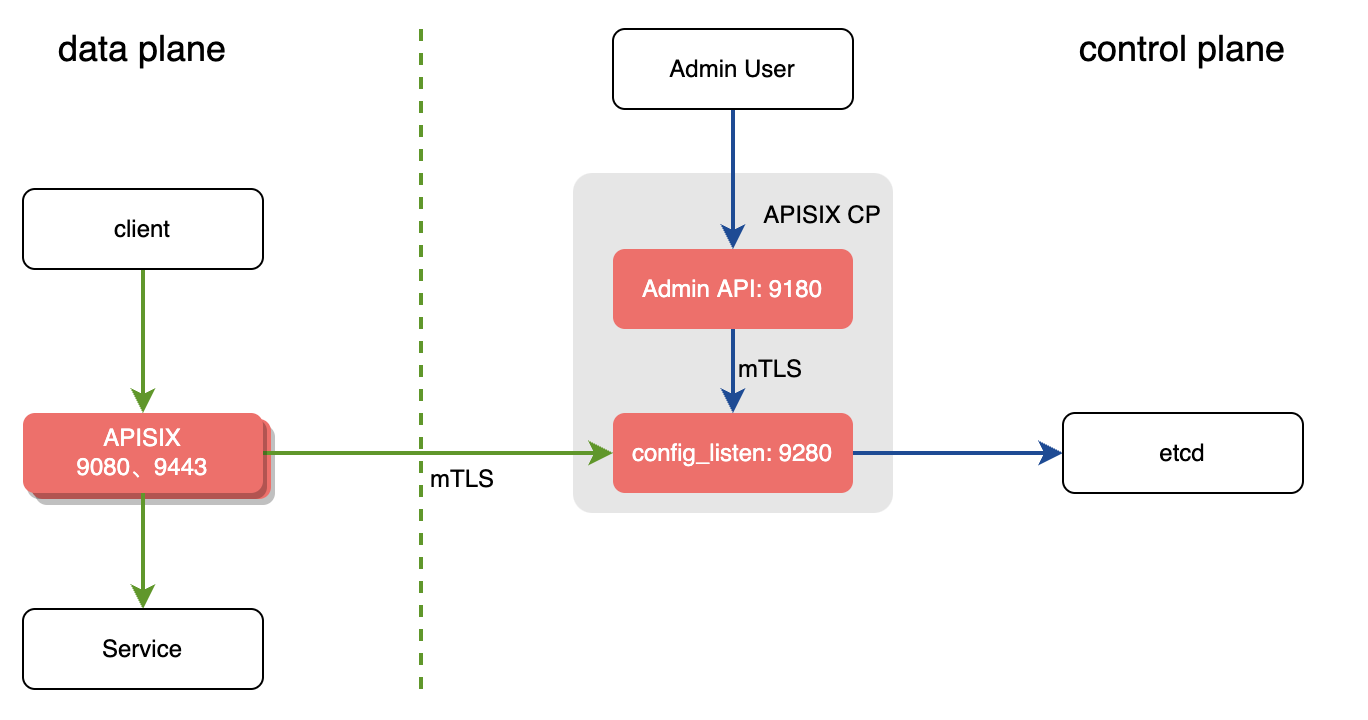
The instance of APISIX deployed as the data plane will:
- Fetch the configuration from the control plane. The default port is
9280. - Performs a health check on all configured control plane addresses before starting the service.
- If the control plane addresses are unavailable, the startup fails and an exception is thrown.
- If at least one control plane address is available, it prints the unhealthy control planes logs, and starts the APISIX service.
- If all control planes are normal, APISIX service is started normally.
- Once the service is started, it will handle the user requests.
The example below shows the configuration of an APISIX instance as data plane in the decoupled mode:
deployment: role: data_plane role_data_plane: config_provider: control_plane control_plane: host: - https://${Control_Plane_IP}:9280 prefix: /apisix timeout: 30 certs: cert: /path/to/ca-cert cert_key: /path/to/ca-cert trusted_ca_cert: /path/to/ca-cert
The instance of APISIX deployed as the control plane will:
- Listen on port
9180and handle Admin API requests. - Provide the conf server which will listen on port
9280. Both the control plane and the data plane will connect to this via HTTPS enforced by mTLS.
The example below shows the configuration of an APISIX instance as control plane in the decoupled mode:
deployment: role: control_plane role_control_plane: config_provider: etcd conf_server: listen: 0.0.0.0:9280 cert: /path/to/ca-cert cert_key: /path/to/ca-cert client_ca_cert: /path/to/ca-cert etcd: host: - https://${etcd_IP}:${etcd_Port} prefix: /apisix timeout: 30 certs: cert: /path/to/ca-cert cert_key: /path/to/ca-cert trusted_ca_cert: /path/to/ca-cert
:::tip
As OpenResty <= 1.21.4 does not support sending mTLS requests, to accept connections from APISIX running on these OpenResty versions, you need to disable the client certificate verification in the control plane instance as shown below:
deployment: role: control_plane role_control_plane: config_provider: etcd conf_server: listen: 0.0.0.0:9280 cert: /path/to/ca-cert cert_key: /path/to/ca-cert etcd: host: - https://${etcd_IP}:${etcd_Port} prefix: /apisix timeout: 30 certs: trusted_ca_cert: /path/to/ca-cert
:::
Standalone
In the standalone deployment mode, APISIX is deployed as a data plane and it reads in configurations from a YAML file (apisix.yaml) in the local file system.
This deployment mode is useful when you have to declaratively define the configuration or when you are using a different configuration center other than etcd.
To configure APISIX in standalone mode:
deployment: role: data_plane role_data_plane: config_provider: yaml